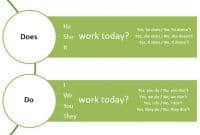
Salam semangat pembaca di mana pun anda berada dan apapun keadaan anda sekarang. Pada bagian ahir dari pembahasan artikel jurnal seri 1 ini, saya akan memaparkan contoh tentang kesimpulan dan saran atau yang lebih mendunia dengan sebutan conclusions and suggestions. Agar pembaca semua biasa menutup artikel jurnal anda dengan mengesankan, maka usahakan kesimpulan dan saran anda jelas, logis, dan mengena. Jelas artinya dalam redaksi penyampainya sebaiknya anda menggunakan diksi yang tepat dan tidak terlalu bertele-tele. Logis maksudnya kesimpulan anda memiliki dasar argument dan data yang jelas sehingga mudah ditelaah oleh pembaca. Dan yang terakhir adalah mengena, mengena dalam hal ini adalah mengenai sasaran dari saran yang anda berikan. Maksudnya, saran yang anda tuliskan haruslah saran yang mudah dimengerti dan jelas target saran yang dituju. Untuk lebih jelasnya, mari berenang-renang di kolam ilustrasi ilmu di bawah ini.
Artikel Bahasa Inggris tentang ERRORS ANALYSIS (conclusions and suggestions)
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
In reference to the result and discussion, it was concluded that:
- The use of simple present tense in students’ descriptive text writing of class X1.A.1 of MAN 1 (Model) Bandar Lampung can be seen from the result that the students used more correct simple present tense (73.81%) than made errors (26.19%) in their descriptive text writing. It means that the students have understood how to use simple present tense in writing descriptive text.
- Even though the students have used more correct simple present tense, but the researcher still analyzed the errors made by the students based on surface strategy taxonomy in order to know the difficulties faced by the students, and it had been found that the most common error committed by the students in their descriptive text writing was omission (50.90%), from 110 items in the form of simple present tense, the students committed 56 items omission error. The students often omitted -s or –es in the verb which the subject of the sentence was in the form of the third person singular and also the students omitted to be when there was no verb in the sentence.
Referring to the conclusions, the researcher comes to the following suggestions:
- The teachers should give much practice about the use of ending -s or –es in simple present tense and explain about how to construct sentences grammatically and appropriately to the students in order to minimize the errors especially in omission errors as the common error in this research, therefore the students can apply their knowledge of simple present tense directly in the real context of writing.
- For other researchers, by seeing the type of errors in using simple present tense in descriptive text writing, they can provide some techniques that can be applied by students to increase the use of simple present tense appropriately in other cases of writing.
REFERENCES
Azar, Betty Schrampfer. 1989. Understanding and Using English Grammar. New Jersey: Prentice Hall Regents.
Brown, H. Douglas. 2001. Principles of Language Learning and Teaching.New Jersey: Prentice Hall Ine.
Burton, Robert Noel. 1986. Analyzing Sentences. London: Addison Wesely Longman.
Cahyono, Djauhari. 1997. Master on English Grammar. Surabaya: Indah.
Corder, S. P. 1976. Introducing Applied Linguistics. Middlesex: Penguin.
Derewianka, Beverly. 1992. Exploring How Texts Work. New South Wales:Primary English Teaching Association.
Dewan Penyunting Penerbit Universitas Lampung. 2008. PedomanPenulisanKaryaIlmiah. Bandar Lampung: Universitas Lampung.
Donald, Robert. 1978. Writing Clear Paragraphs. New Jersey: Practice-Hall, Inc.
Dulay, H., Burt, M. and Krashen, S. D. 1982. Language Two.New York: OxfordUniversity Press.
Finocchiaro, M. 1989. The Functional-Notional Approaches from Theory to Practice.New York: Oxford University Press.
Greenbaum, Norman. 1993. Advance Grammar in Use. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Grace, Eudia and Sudarwati. 2002. Look Ahead (An English Course) for Senior High School Students Year XI. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Hammer, Jeremy. 2004. How to Teach Writing. London: Longman.
Harris, David P. 1974. Testing English as A Second Language. New York: Tata Mc. GrawHill Publisher Co. Ltd.
Heaton, J. B. 1990. Language Testing Modern English Publications.London:Longman.
Hendrickson, James M. 1982. Error Analysis and Error Correction in LanguageTeaching.Singapore: Seamoe Regional Language Centre.
Hewings, Martin. 1999. Advanced Grammar in Use (A self-study reference and practice book for advanced learners of English). Jakarta: Erlangga.
Hornby, A. S. 1986. Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary of Current English. Oxford University Pers.
Indrati, Ida Ayu. 1998. An Analysis of Tenses Errors in Students’ Writing “Case Study” at Class II.5 of SMUN 2 Bandarlampung. Bandarlampung: Script (Unpublished) Lampung University.
Krashen, S. 1988. The Input Hypothesis: Issues and Implications. London: Longman.
Krohn, Robert. 2002. English Sentence Structure. Jakarta: BinarupaAksara.
Laru, R. 2010. Concept of Grammar.Jakarta: Yudhistira.
Linderman, E. 1983. What is Writing in A Rhetoric for Writing Teachers. London: The University of Chicago Press.
Masito, Emmi Riasari. 2004. The Students’ Descriptive Writing Ability at the First Grade of SMU AL-Kautsar Bandar Lampung.Bandarlampung: Script (Unpublished) Lampung University.
Master, Peter. 2004. English Grammar and Technical Writing. Washington: Office of English Language Program.
McKay, S. 1987. Teaching Grammar: From Function and Technique. Hemel Hempstead: Prentice Hall.
Murcia, M., and Hilles S. 1995. Techniques and Resources in Teaching Grammar.New York: University Press.
Muhammad. 2009. The “s” of Third Person Singular in the Simple Present Tense:
From Rote Learning to Classroom Efficient Practice the Case of First Year Students .Solo: Script (Unpublished).
Nichols, Lorrain. 1993. Grammar Step By Step. Jakarta: BinarupaAksara.
Prayogo, Irawan. 2012. An Analysis of the Students’ Proficiency in Descriptive Paragraph Writing at the Second Grade of SMA Tri SuksesNatarLampung Selatan.Bandarlampung: Script (Unpublished) Lampung University.
Reid, M. Joy. 1994. The Process of Paragraph Writing. New Jersey: Practice Hall, Inc.
Sari, Pusvita. 2009. Improving Students’ Achievement in Learning Simple Present
Tense through Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) at the First Year
of SMPN 5 Bandar Lampung. Bandarlampung: Script (Unpublished)
Lampung University.
Setiyadi, A. G. Bambang. 2006. MetodePenelitianUntukPengajaranBahasa Asing: PendekatanKualitatifdanKuatitatif. Yogyakarta: Penerbit Graha Ilmu.
Setiyadi, A. G. Bambang.2003. Teaching English as a Foreign Language. Yogyakarta: PenerbitGrahaIlmu.
Slamet and Tim Edukatif HTS. 2008. Modul Bahasa Inggris. Surakarta: CV Hayati Tumbuh Subur.
Smalley, L., Regina, and Ruetten, Mary, K.1986. Refining Composition Skills. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Suhesti, Ganis. 2012. Teaching Descriptive Text through Cooperative Learning by Using Roundtable technique at the First Year of SMA XaveriusPringsewu.Bandarlampung: Script (Unpublished) Lampung University.
Sulaiman. 1970. Practical English Grammar. Surabaya: Indah Press.
Susanto, Andreas. 1997. A Comparative Study between Spoting the Difference Game and Dialogue towards Students’ Achievement in Present Perfect Tense Script. Bandar Lampung: Script (Unpublished).
Tarigan, Henry Guntur. 1988. PengajaranPemerolehanBahasa. Departmen PendidikandanKebudayaan. Jakarta: Direktorat Jendral PendidikanTinggi, P2LPTK.
Thomson, A. J. and Martinent A. V. 1992. Fundamental of English Grammar. New York: Prentice Hall.
Trask, R. L. 1999. Key Concepts in Language and Linguistics. New York:Routledge.
Veit, Allsop. 1986. Making Sense of English Grammar. Jakarta: Binarupa Aksara.